edu.sa
sch.sa أو edu.sa
HTTPS
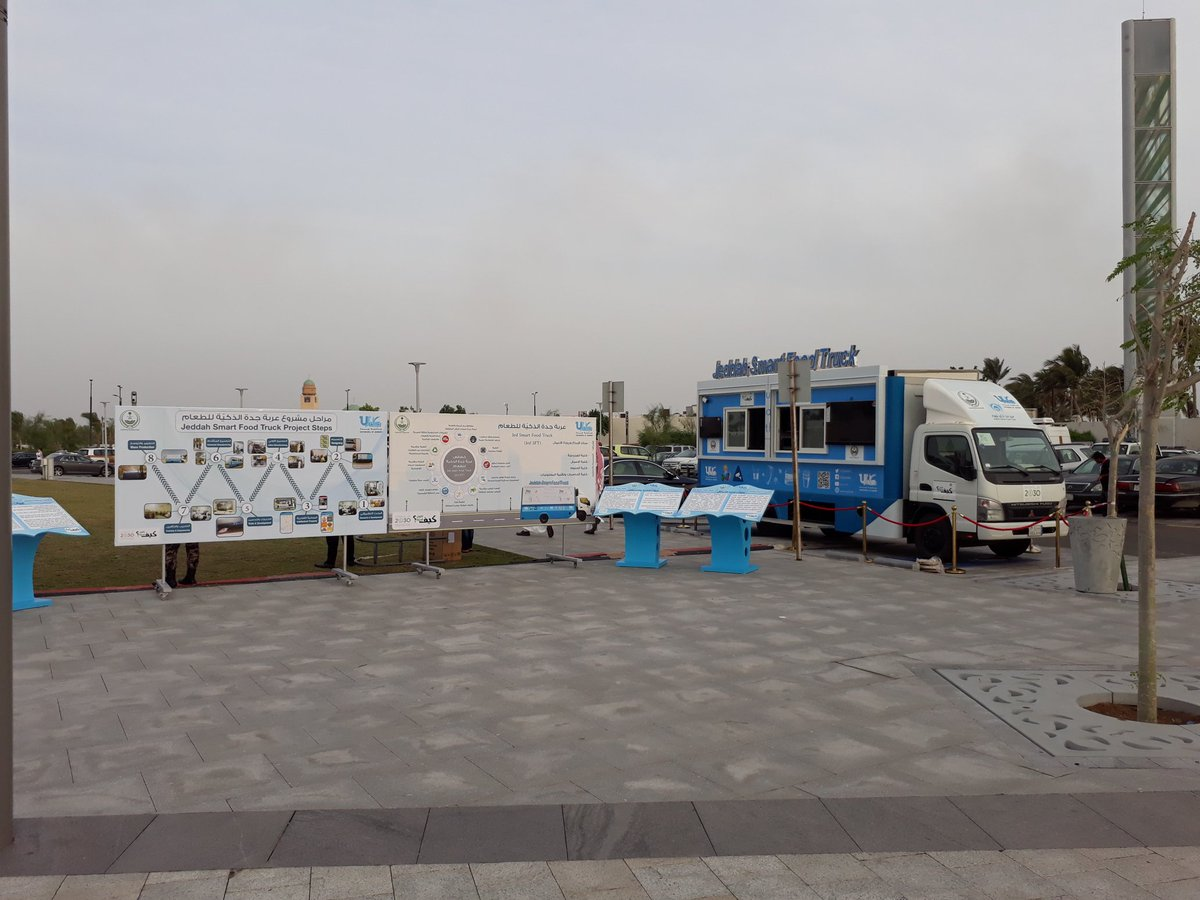

In fulfillment of Jeddah University's social responsibility, this smart food cart model is presented as an example of the economic feasibility of establishing smart mobile food cart projects. Food carts differ from restaurants in that they are difficult to ensure food safety. Without the ability to inspect mobile food carts during actual operation, the proliferation of carts could become a negative factor affecting food safety, potentially leading to foodborne illness or death. The smart food cart concept presented by Jeddah University involves developing a mobile application that connects customers, distributors, and local authorities. A wireless communication system and equipment will also be developed to connect the cart to the proposed application to serve both customers and local authorities. This development of the proposed application will help suppliers sell a variety of products, as food suppliers will advertise and publish menus through the proposed application. Service providers can also attract customers by displaying images of their products. Suppliers can also add arrival and departure times from a specific area, which will help their followers know their availability, thus saving both time and money. Local authorities will be able to monitor carts in an economically efficient manner and monitor the quality of the products provided by monitoring the indicators and sensor readings inside the cart. Customers will also be able to locate the service provider, view the menu, and easily order their favorite food. Potential health problems resulting from food contamination during handling are monitored and controlled through a risk control point system and food safety procedures that must be followed during operation. Temperature sensors are installed in refrigerators, coolers, and storage areas, as well as sensors to detect pollutants and air quality. Monitoring devices are stored in the health inspector's kit, which includes a bacterial contamination and general hygiene device (System Sure Plus), which is used to measure contamination levels in water and surfaces. The device also includes an En-Sure device, which is used to measure contamination levels in water and surfaces, in addition to microbiological tests such as the number of E. coli bacteria, infrared thermometers, a pH meter, and a frying oil shelf life tester.